Peroxide b6 vitamin for weight loss: Vitamin B6 is required for a variety of Biological functions. It’s so adaptable! Over 100 enzymatic pathways are affected by vitamin B6! Vitamin B6 is important for weight loss since it helps with protein, carbohydrate, and fat metabolism! Vitamin B6 also helps to keep homocysteine levels in check. Homocysteine is an amino acid found in the blood.
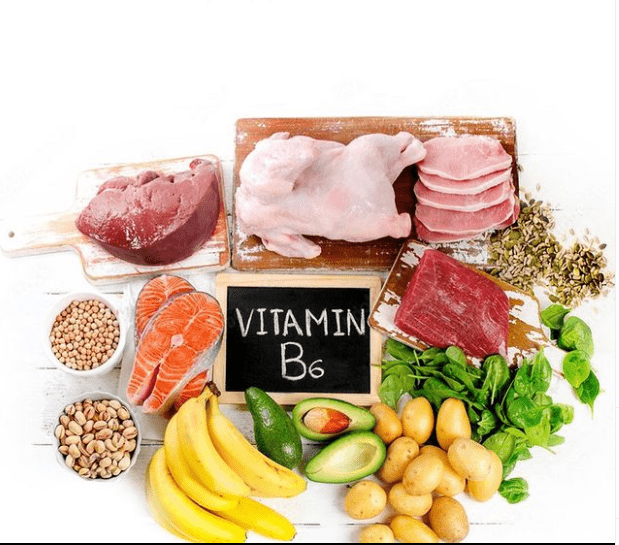

Homocysteine levels above a certain threshold are associated with obesity, BMI, and hypertension! Vitamin B6 is needed for glucose metabolism and insulin secretion as well. Vitamin B6 is also necessary for obese persons to avoid insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Obese people are 80 times more likely to develop type 2 diabetes than those with a BMI under 22.
What Is the Process?
The water-soluble forms of vitamin B6 are pyridoxine, pyridoxal, and pyridoxamine. It is necessary for your health and performs a variety of functions in your body. Vitamin B6 is required by about 100 enzymes involved in protein metabolism, for example. It is also necessary for the metabolism of RBCs. Vitamin B6 is required for the neurological and immune systems, as well as the conversion of tryptophan (an amino acid) to niacin (a vitamin). Red blood cells are responsible for transporting oxygen to tissues. Vitamin B6 is required by hemoglobin. Vitamin B6 also aids the transport of oxygen by hemoglobin.
The immune system of the body goes through a series of metabolic changes in order to fight infections. White blood cells combat infections and are made up of calories, protein, vitamins, and minerals. Vitamin B6 is necessary for immune system function because it aids in protein metabolism and cell proliferation. It helps your lymphoid organs stay healthy (thymus, spleen, lymph nodes). Vitamin B6 deficiency has been shown in animal studies to impair antibody production and immunological response. Vitamin B6 also aids in the regulation of blood sugar levels.
The Link Between Vitamin B6 and Heart Disease
Homocysteine, an amino acid found in the blood, can be raised by a shortage of vitamin B6, folic acid, or B12 [28]. Homocysteine levels above a certain threshold have been linked to heart disease and stroke. High levels of homocysteine can damage coronary arteries or make platelet clumping and clotting easier. However, there is no evidence that taking vitamins to lower homocysteine lowers the risk of heart disease. Supplementing with vitamin B6, folic acid, and vitamin B12 may help protect against coronary heart disease.
Too much vitamin B6 may cause nerve damage in the arms and legs. Excessive vitamin B6 intake usually causes this neuropathy, which is reversible. According to the Institute of Medicine, this includes doses of less than 500 mg per day. The Food and Nutrition Board of the IOM suggested a daily upper intake level (UL) of 100 mg for all people. “Unfavorable outcomes rise as intake surpasses the UL.” Vitamin B6 is required for several neurotransmitters, including serotonin and dopamine.
They’re required for normal nerve cell communication. Low vitamin B6 levels have been associated with seizures, chronic pain, depression, headaches, and Parkinson’s disease. Serotonin levels are decreased in migraine and depression sufferers. However, vitamin B6 supplements haven’t solved these issues so far. In one study, a sugar pill reduced headaches and melancholy associated with low-dose oral contraceptives and vitamin B6.
B12 and B6 Nutritional Injections for Weight Loss
Dr. Stanley Bernstein is a big believer in B6 and B12 injections for weight loss. Dr. Bernstein has 25 years of experience conducting weight loss clinics in Ontario. His diet is a one-of-a-kind regimen that includes injections and requires no physical activity. Bernstein’s diet is medically supervised and consists of more than just calorie counting. “We give our patients a lot of vitamins and minerals.” Vitamins are administered in some cases.” Clients receive a B6/B12 injection three times each week.

The vitamins are thought to aid in fat digestion. “B vitamins assist people in sticking to their diets,” Bernstein said. “I find that they assist me in losing weight.” Every week, our patients drop four to five pounds.” Losing weight can be pricey. Initial consultations cost $195-$235, with services and injections costing $100 every week. According to Bernstein, a patient who loses 35 pounds will spend roughly $1,000.
FDA and Other Organizations’ Concerns
B12 injections, according to the American Society of Bariatric Physicians, “do not aid in weight loss and do not function.” The Food and Drug Administration runs a consumer webpage to assist consumers in better understanding vitamins and their potential. Cobalamin (vitamin B12) is required for good health. Weight loss has also been linked to B12. It is essential to generate DNA, the genetic material in all cells, and it helps maintain nerve and blood cells healthy. The protein binds to vitamin B12.
All of these B vitamins help the body convert carbs into glucose or sugar, which is subsequently utilized to generate energy. The breakdown of lipids and proteins requires these B vitamins. They protect the digestive tract and mouth mucous linings, as well as the nervous system, liver, skin, hair, and eyes. Cobalamine is an excellent anti-stress vitamin since it strengthens the immune system and assists the body in dealing with stress. B12 injections have been found to improve general health and energy. They also assist the thyroid in regulating energy levels. The diuretic effects of B12 aid to reduce water retention. Fish, milk and milk products, eggs, pork, and poultry all contain vitamin B12.
Breakfast cereals with added vitamin B12 are particularly good for vegetarians. Dietary alternatives are suggested in the table of recommended vitamin B12 food sources. Although most adult Americans obtain enough vitamin B12 through their meals, some people are unable to absorb it. People who do not consume meat or fortified foods are also susceptible. The majority of patients who have a vitamin B12 deficiency have a stomach or intestinal illness that limits vitamin B12 absorption. B12 deficient anemia is sometimes the only indication of digestive problems. Cells that secrete stomach acid and intrinsic factors are frequently killed during gastrointestinal surgical operations.
Heart Disease and Vitamin B12?
Homocysteine, an amino acid found in the blood, can rise if you don’t get enough vitamin B12, folate, or B6. Heart disease and stroke are both linked to homocysteine levels. High levels of homocysteine can damage coronary arteries or make platelet clumping and clotting easier. However, there is no evidence that taking vitamins to lower homocysteine levels lowers the risk of heart disease. Supplementing with vitamins B12, folic acid, and B6 may help prevent coronary heart disease.
How much B6 do we require on a daily basis?
Both men and women need 1.3 mg of vitamin B6 every day. Vitamin B6 is needed more by the elderly! Vitamin B6 should be taken daily by women over 51 and men over 1.7 mg. Vitamin B6 requirements for lactating mothers are 1.9 mg and 1.9 mg per day, respectively.
B6-fortified foods
Many foods contain vitamin B6. As a result, vitamin B6 deficiency is extremely uncommon! Food provides 1.5 mg of vitamin B6 to women and 2 mg to males per day. Vitamin B6 is abundant in meat and fish. Vegetarians and vegans can acquire adequate vitamin B6 from this diet.
FINAL CONCLUSIONS
The best way to maintain a healthy weight is to combine a balanced diet rich in veggies, protein, and good fats with frequent exercise. Short-term vitamin B6 supplements may help if your levels are low. Always discuss dosage and safety with your functional medicine practitioner.