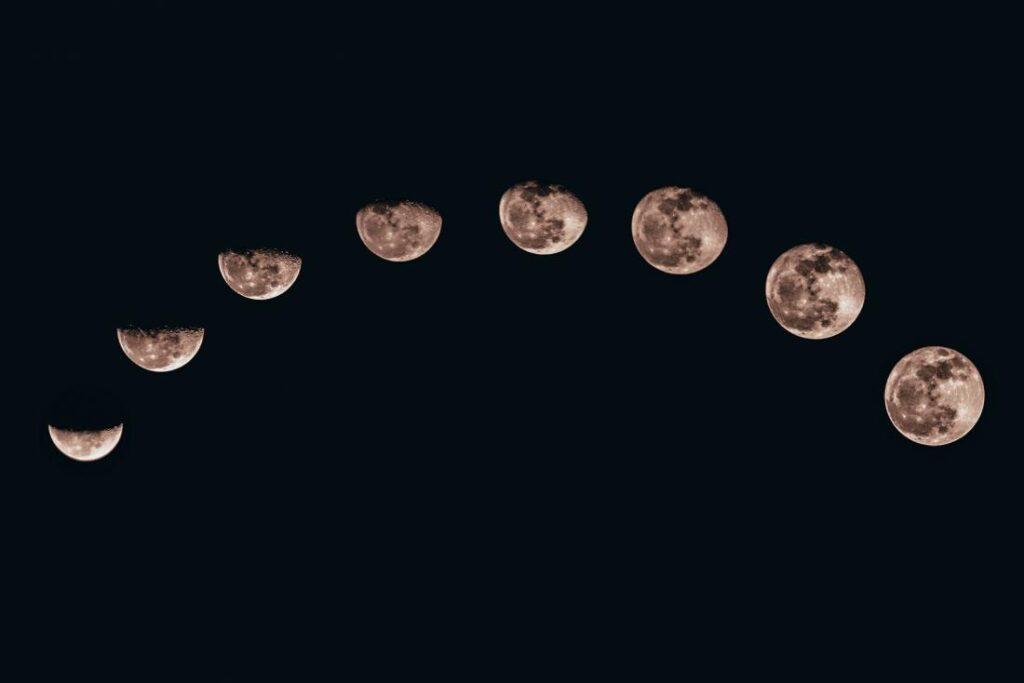
Recurring Shapes Of The Moon Illuminated By The Sun: (Defining the phases of the moon) Take a close look at the picture. Use everything you’ve studied about Moon Phases to describe what the image depicts and what causes them in the space provided below. The moon does not give forth any light of its own.

It sparkles because of its shiny surface, which reflects the sun’s rays. to the ground. Only half of the moon’s surface that faces the sun receives sunlight. The position of the sun, Earth, and moon in space changes as the moon moves around the Earth. For instance, there are situations when between the sun and Earth is the moon (new moon). When the Earth is in the way of the sun and the moon, a full moon appears. The Earth, the moon, and the sun can form a triangle from time to time. Based on its position relative to the sun, a lunar phase is determined. As well as the planet itself. As the moon circles around the Earth, different parts of the sunlit surface of the moon are illuminated at different times of the day.
Viewable from the planet’s surface. As a result, the moon’s appearance changes from night to night when viewed from Earth. The moon’s apparent form and location in the sky vary throughout time. The way it’s constructed also contributes to this. movements in the universe The Earth’s rotation accounts for the shift in location during the course of a single night. The rotation of the Earth’s axis from When viewed from the west, it seems as though the sun rises at an eastern latitude and sets at an eastern latitude. However, The moon rises and sets at a significantly different time each day, despite little variation in the sun’s time of day.
Duration of Moon Between Earth’s orbit
in different ways. About every 13 to 15 days, the moon advances eastward as it completes one revolution around the Earth. Every 24 hours, the Earth’s orbit moves by one degree. As a result, the moon rises an hour later each night than it does during the day.
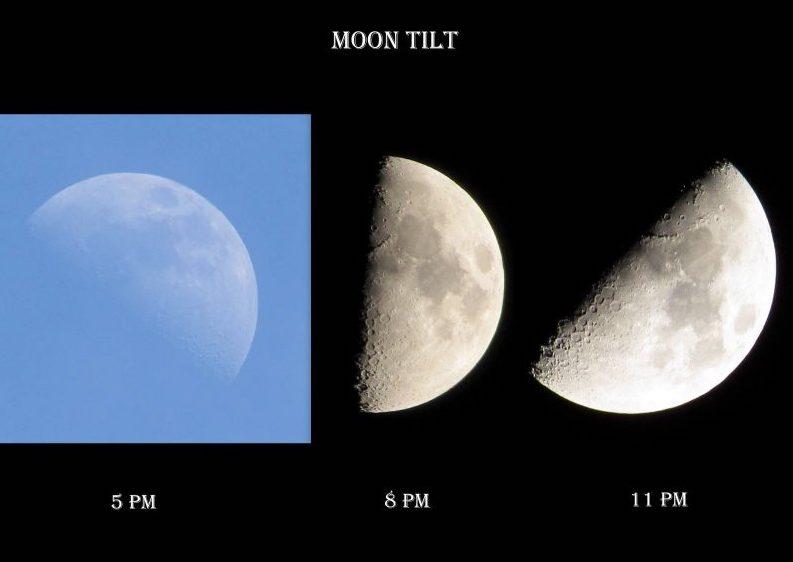

Moonlight and its apparent size will vary depending on its distance from the Earth during the full moon phase; in case it is at the farthest point known as lunar apogee it will result in the smallest or micro full moon, and if it is closest to us known as lunar perigee it will result in the macro full moon – a term coined by astrologer Richard Nolle in 1979. For the two extreme points of the moon, apogee, and perigee, theoretical formulas are obtained for the earth’s lunar luminous fluxes, which represent the strength of the moon’s light that the earth intercepts in the direction normal to the incidence over a one-square-meter region. Also included are the formulas for calculating the apparent diameters of full moons at each of these locations.
In accordance with the given numbers, the full perigee moon seems to be 29 percent brighter and 14 percent larger than the full apogee moon. Keywords. theoretical estimate, pedagogical theory, micro moon luminous flux There is nothing we can do for you We’ve all seen the Moon at some point in our lives, and it’s a familiar sight. The moon, moonlight, the moon’s phases, the full moon, and solar and lunar eclipses have fascinated mankind for as long as they have been on this planet.
Prior to that: It takes the moon 27.3 days to complete one orbit of the Earth. There are 29.5 days in a whole lunar cycle, though. This discrepancy in As Earth and the sun orbit each other, the moon completes a full orbit and a whole cycle of phases. as to catch up with its relative starting position, the moon must go a little further around Earth. Humans, navigators, astronomers, and astrologers have been fascinated by the phases of the moon since the dawn of humanity. elliptical orbit and the fact that its plane is inclined to the Earth’s rotational axis cause new moons, full moons, and eclipses of the sun and moon.
Moon’s appearance varies so dramatically
Not only does the moon’s location matter, but so do the sun’s and Earth’s. All of our solar systems revolve around the sun at an elliptical rate of 0.0167 revolutions per year, and the Earth revolves on its own axis as well. And all this is going on while our neighboring satellite, the Moon, travels in a round orbit 29.53 days in length around the Earth, rotating on its own axis.

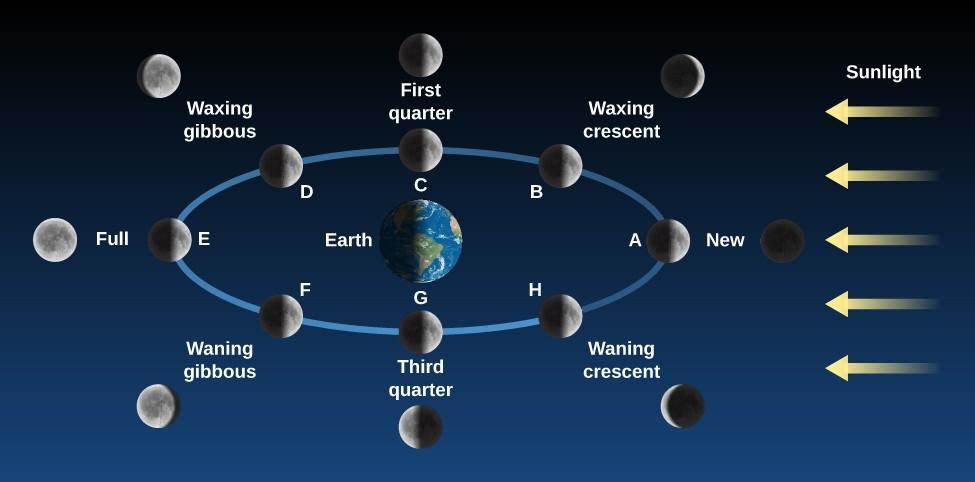
The phases of the moon, solar and lunar eclipses, and ocean tides are all caused by changes in the location of the moon, the earth, and the sun. For folkloristic or religious purposes (e.g. astrology or the Islamic or Hindu calendars), lunar phases are still utilized in the earliest calendars. The sun always illuminates half of the moon. We can see different areas of the lit area as the moon moves around the Earth. As the moon orbits the Earth, it appears as if its shape is constantly shifting. Because we see the lit portion of the moon’s surface from a variety of angles, we see it differently. These are referred to as “moon phases.” Every 29.53 days, the moon cycles through a variety of different shapes. depicts the lunar phases in order from the new moon to the full moon, from waxing gibbous to waning gibbous to the last quarter, from declining crescent to new moon once more.
Phases 0 percent, 25 percent, 50 percent, 75 percent, 100%, 50 percent, and 25 percent are each represented by a percentage of the moon’s illuminated surface which is shown in Fig. 2(b). Due to a 5.145-degree angle between the moon’s revolutionary plane and the Earth’s rotational plane, a full moon phase could be feasible. This is why lunar eclipses don’t happen more frequently because the moon is above or below the Earth throughout most months. During the night, the moon’s reflection of Sun rays illuminates the Earth dimly. As the overall flux or perceived intensity of light striking or passing through an object, luminance is the photometric term used to describe this light.
Model of Human Brightness Perception
The luminosity 1 function, a standardized model of human brightness perception, is comparable to the radiometric unit watts per square meter. Light intensity is measured in lumens per square meter (LU/m2). There have been some attempts in the past to quantify the value of this moonlight, which is loved by everyone, even students and professors of physics. 2,3 in educational publications, research journals, and handbooks, both theoretically and empirically.
Both the moon’s phase and its albedo, which is defined as the ratio of the total amount of light reflected back to that incident on the moon, determine how much light makes it to Earth. Earth, Moon, and Sun are all in alignment at full moon, however, the moon is on the other side of our planet, so it is facing us. (Xanax) We’re tidally locked to the moon because we see the same lunar surface every time. Invisible to the naked eye is the darkened section. Lunar apogee and lunar perigee have a significant effect on the size and luminosity of a full moon; a micro full moon will be the smallest and a macro full moon will be the largest, while a super full moon will be the brightest.
Astrologer Richard 6 Nolle first used the term “super moon” in 1979 to describe a full moon at perigee-syzygy, when the moon is at or near (within 90% of) its closest approach to the Earth in a given orbit. This is a rare occurrence. The purpose of this study is to estimate and compare the apparent diameters of these two moons, as well as the luminous fluxes from the micro full moon and super moon, as seen from the Earth’s perspective.




