Cold Laser Pain Relief: Our laser therapy equipment, which we produce and sell ourselves, has applications in the treatment of acute and chronic pain, wound healing, fracture healing, arthritis, the management of skin and mucosal ulcers, a variety of chronic inflammation, nervous headache, dysfunction, rheumatism, infective/non-infectious inflammation, and dermatosis. Cold Laser therapy, also known as low-level laser therapy (LLLT), employs a low-intensity laser to treat wounds and pain.
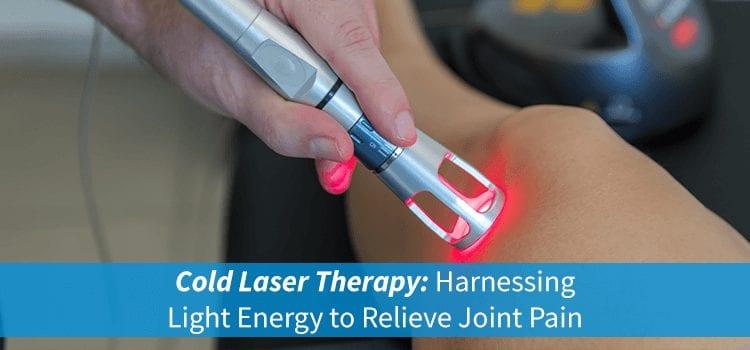
Instead, you can invest in the best cold laser therapy device on the market and use it at home, where you’ll have more control over your treatment schedule. To operate the machines safely, you should always adhere to the manufacturer’s instructions or schedule a visit from a representative. By penetrating 5 centimeters into your skin, this procedure uses laser light to heal your cells and speed up your metabolism.
How exactly does cold laser therapy operate?
Low-level light is applied directly to the area of concern during cold laser therapy. When this light is absorbed by the skin, a reaction takes place that regenerates the harmed cells. The light’s non-thermal photons, which reach deep into the skin and dermis, can facilitate dermal and epidermal metabolism. The healing process is accelerated as a result of this. Cold laser therapy uses particular light wavelengths to hasten the healing process. For general healing, a wavelength between 600 and 700 nm is frequently used. For deeper tissues, a wavelength between 780 and 950 nm is employed.
CLT has been in existence for a while. The idea that light can be amplified through a process known as stimulated emission of radiation was first put forth by Einstein in the early 1900s (LASER). 51 years after the first laser was created, Professor Andre Mester started using low-power lasers to treat his patients. It had never before been used in medicine in such a significant way as this treatment.
According to the Therapeutic Principle
Our laser therapy equipment provides two laser irradiation modalities: a 200mW laser shower head and a 5mW laser probe, both with 810nm wavelengths. The laser of these wavelengths poses no risk to human tissue or cells, but it can pierce skin, fat, and blood vessel walls. Blood absorbs about 10% of the laser’s energy during laser irradiation. Low-level laser therapy has been proven in clinical studies to speed wound and tissue repair, increase blood flow, enhance neuron function, and have anti-disease properties.
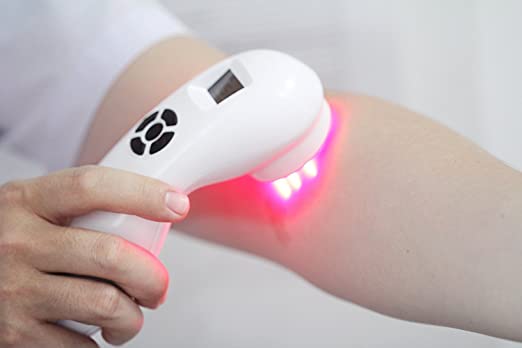
Low-level laser therapy (LLLT), also referred to as photobiomodulation therapy or cold laser therapy, is an effective treatment for a number of ailments (CLT). By exposing the injured tissues to specific light wavelengths, healing can be sped up. Medical professionals may use treatment for patients with acute or chronic diseases. The most frequent adverse effects of cold laser therapy are pain, swelling, and spasms. This symptom relief allows many patients to get back to a more functional state.
- Accelerate the growth of granulation tissue and blood vessels, increase protein synthesis, encourage the sedimentation and cross-linking of collagenous fibers, and promote the formation of blood clots to quickly heal wounds.
- Boost lipoprotein lipase activity, improve red blood cell deformability and oxygen-carrying capacity to activate and purify the blood, lower blood fat and viscosity, and regulate blood pressure.
- Increased blood circulation will improve the metabolism of circulating substances and expand the capacity of the cerebrovascular blood supply.
- Increase the metabolism of enkephalin, boost endorphin release, and fortify the immune system by recirculating leukomonocytes to enhance the phagocytic activity of macrophagocytes to lessen inflammation and odynolysis.
The FDA has categorized medical lasers into three groups. The strongest of all is class 4 surgical lasers, which are used by doctors to sever tissue. Medical lasers don’t come in any other “painful” varieties. The following category of lasers is Class 3B non-surgical lasers, which do not cause pain or burning sensations. On the other hand, this family of lasers has the ability to penetrate deeper and treat diseases of the joints and deep tissues.
Cold Laser Therapy (CLT): How Effective Is It?
In a nutshell, yes. The longer answer is yes, but we’re still unsure of the full scope of its effectiveness. Clinicians have long used CLT as a minimally invasive technique to treat pain in their patients. Over the past 50 years, the topic has been the focus of countless studies by medical experts. These studies suggest that CLT is a secure and reliable pain-relieving therapy. All of these studies use double-blinded, placebo-controlled variables as comparison points.
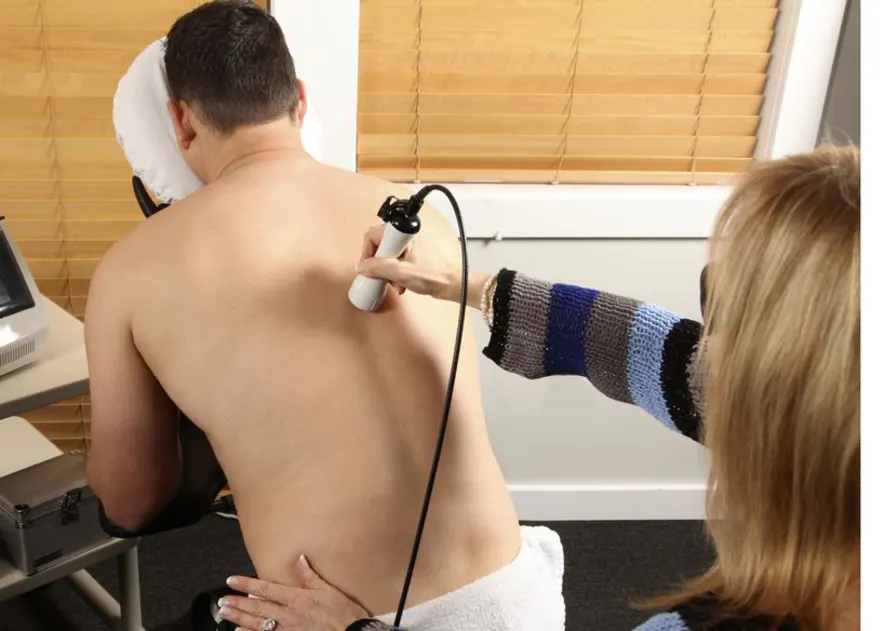
The two most significant aspects of CLT that are poorly understood are the dosage and the number of sessions. This may be due to a combination of patient biochemistry and the wide range of diseases that CLT treats. There is therefore strong evidence that CLT benefits people with both restricted and unrestricted health problems.
Do I qualify for cold laser therapy (CLT)?
There is no right or wrong response when it comes to medical procedures. Patients with malignant lesions or carcinomas are advised against undergoing the procedure. Additionally, CLT should never be performed on pregnant women. Pregnant women who are exposed to CLT should be tested to see if CLT is present in their unborn children as a precaution. To ascertain whether CLT is suitable for your specific circumstance, speak with your doctor. Your medical background and any existing conditions must be disclosed to him or her. In order to fully comprehend your condition, ask your doctor as many questions as you need to.
Do you experience recurring pain in your joints or anywhere else in your body?
CLT may be an option if this is the case. Additional information can be obtained by contacting NJSO at (866) 553-0612. Minimally invasive and conservative procedures are the specialty of our orthopedic surgeons. We guarantee that you’ll get the treatment that’s suited for you.
Are there any side effects of Cold Laser Therapy?
CLT may be used on any sort of cell, making it extremely versatile. Because of this, CLT is a potential therapy option for a wide range of illnesses. Listed below are some common ailments that can be helped with CLT: Arthritis is the inflammation of a joint or joints in the body in its most basic form. It could be a result of wear and tear on the cartilage, or it could be an autoimmune illness (such as rheumatoid arthritis) (such as rheumatoid arthritis). It can take many different shapes. Pain, stiffness, and swelling are all hallmarks of rheumatoid arthritis syndrome. As a result of its role as a weight-bearing joint, the knee is the most commonly affected by arthritis.
As a widespread yet complex chronic pain illness, fibromyalgia is characterized by pain and tenderness all throughout the body. The exact cause of fibromyalgia is unknown, and the severity of symptoms varies from person to person. Mental health issues, such as sadness and inability to focus, are common in this illness. When tendons become inflamed, they lose their ability to hold bones and muscles together. This condition is known as tendonitis. Minor, repeated collisions in the same place over time are the most typical cause of this injury.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: The major nerves in the hand are compressed as they pass through the wrist in cases of carpal tunnel syndrome. Hand and arm pain, numbness, and tingling are common symptoms. Without therapy, this illness usually worsens. Carpal tunnel syndrome sufferers can take heart: CLT has been shown to provide relief. Chronic back pain and musculoskeletal pain are two other illnesses that can be helped with CLT. For mild sprains and strains, some doctors utilize CLT to speed up the healing process.

