What Do Decomposers Secrete To Break Down Organic Matter: A decomposer breaks down the organic components of dead creatures in order to produce energy. These organisms are typical examples of recyclers seen in nature. Examples include all types of organisms, such as bacteria, worms, and fungi. They eat detritus, which is Latin for “garbage.” They are essential to the process of Nutrient cycling. Consumers will use their bodies as a type of energy storage by storing the energy of the prey.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Decomposer
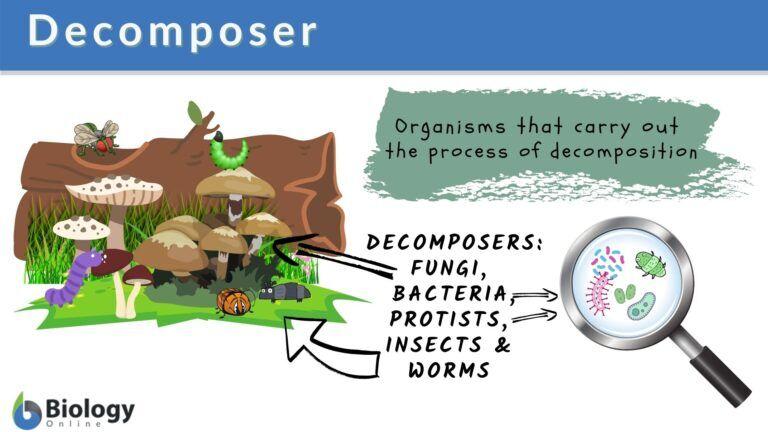
Decomposers break down dead people’s body parts to replenish the environment with minerals and other resources. Nitrogen, phosphorus, and carbon are essential elements for a healthy ecosystem. All three are present in plant and animal deterioration. Decomposers play a critical function in ecosystems by recycling nutrients to keep other organisms alive.
What Are the Decomposers?
These organisms are typical examples of recyclers seen in nature. They disintegrate dead materials and ecosystem waste in order to recover energy and other valuable components. If you step outside right now, you will undoubtedly discover one in the ground. Worms are a well-known example of how this idea works. These guys are really good, despite the fact that they are a little odd. Flowers and other plants work to break down and nourish the soil, which allows them to flourish. The dead items they devour are referred to as detritus. This energy source also provides most ecosystems with minerals and fertilizer.
A decomposer is a creature that engages in the natural process of decomposition while consuming decaying organisms in order to recycle nutrients, according to biology. I can think of a few decomposers. Two of the ecosystem’s most significant decomposers are bacteria and fungi. Everyone is puzzled by the meals of decomposers. On the other hand, decomposers eat deteriorating materials.
Why are these decomposers so important?
These organisms, which are a vital part of the ecosystem’s food chain, recycle the organic and nutritive material of the dead in order to maintain the ecosystem’s health. All of this organic and nutrient material is consumed or absorbed by plants or other ecosystem producers before returning to the food chain. Below is an illustration of how decomposers interact with the ecology.
Saprophytes or decomposers, which consume the dead matter and disassemble it into important molecular components like carbon, calcium, and nitrogen that may be present in the soil, are a significant part of soil ecology. In contrast to other animals, saprophytes carry out digestion ex vivo, or away from their own bodies. Saprophytes produce digestive enzymes to assist in the breakdown of the organic dead material. Saprophytes all break down the amino acids from proteins, the simple sugars from carbohydrates, and the fatty acids and glycerol from lipids/fats.
All of these saprophytes share the following characteristics:
- Are there any strands on you?
- Missing are the roots and stem.
- It is a non-phototrophic organism as a result.
- Create spores of your own own.
The importance of the work they conduct is beyond question. Without decomposers, it would be impossible to reuse trash and dead materials. Decomposition is the process by which a dead organism’s complex organic component is transformed into a simpler form, and it is the decomposers’ responsibility to disassemble and decompose the deceased creature. In environmental science or ecology, there are many different animals and plants that contribute to the process of decomposition.
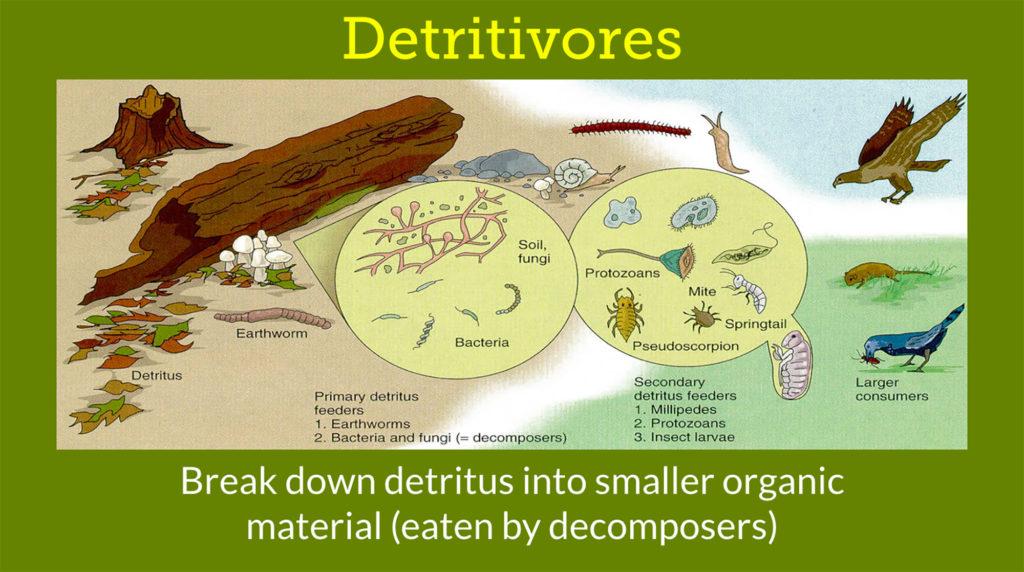
Decomposers and Detritivores
Organisms that break down organic materials are referred to as composters. Two of the most prevalent categories of decomposers in nature are detritivores and saprotrophs. Saprotrophs, on the other hand, include bacteria and fungi that break down organic substances. Despite the fact that they are frequently used synonymously, decomposers and detritivores are distinct ideas. When utilizing the term “decomposer,” saprotrophs and detritivores are both referred to as such.
The significance or purpose of Decomposers
Cleaning and balancing that is kind to the environment: For the ecosystem to work correctly, dead animals must be decomposed by decomposers. The natural cleansers that decompose the remnants of the deceased are known as decomposers, and they can be either plants or animals. Decomposers work to break down the dead, creating an environment for new life. Decomposers are therefore essential for preserving the ecosystem’s balance.

Recyclability of nutrients:
Decomposers disassemble dead matter into its constituent elements, such as carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorus, and then release these substances into the environment for plants to absorb. This process recycles the nutrients that the dead matter once contained. They can be ingested and utilized by plants and algae as sources of energy for growth and development. Decomposers like carbon dioxide, nitrogen, and sulfur supply the essential ingredients that food chain producers depend on. Decomposers perform a significant function despite being at the bottom of the food chain.
Food chain illustration
There are three basic types of organisms based on what they eat: A food chain has several different trophic levels. There are species that use a similar feeding technique at every level of the food chain (or ecological pyramid). Living things can be categorized into three main groups according to their eating habits. The producers, consumers, and decomposers of matter are all present here. Producers, not consumers, receive their nutrition from inorganic sources. Humans consume organic materials. Organisms that degrade organic substances are referred to as “decomposers.”
Decomposers’ types
The four primary categories of decomposers that you should be familiar with are fungi, insects, earthworms, and bacteria. A creature that consumes waste is a scavenger. Saprophytes secrete the enzymes that decompose organic matter, which is ultimately consumed by other organisms. Microorganisms like bacteria and fungi are examples of saprophytes. Organic material is broken down differently by detritivores than it is by decomposers.
Fungi:
A fungus is not a phototroph. Despite not participating in photosynthesis, they are the main decomposers in the environment. Other creatures, like algae, do not decay; in fact, algae produce because they possess pigments necessary for photosynthetic activity. Producers are algae. As a result, fungus act as the food chain’s decomposers while algae act as its producers.
Insects:
Fly larvae, maggots, and ants are just a few of the insects that are crucial to decomposition in nature. Due to the fact that they ingest their own waste during digesting, insects are categorized as detritivores. Different species of insects contribute to the breakdown process.
Earthworms:
Oral detritivores are animals that ingest dead things and feces, both from plants and animals, and then break them down in their intestines to break down the litter.
Bacteria:
Due to their ubiquitous nature, these microscopic organisms are the kings and queens of disintegration. The most commonly asked query, “Are bacteria decomposers?” has been addressed as a consequence. By recycling nutrients like nitrogen and carbon and making them available to producers, bacteria play a significant role in the food chain. Any organism that eats its own waste is a saprotroph.
Conclusion
The detritivores and decomposers are a crucial group of organisms in the breakdown of organic materials in ecosystems. An organism that is both a detrivore and a breakdown agent is said to be heterotrophic. They are detritivores, which are decomposers. Detritivores ingest organic matter in the form of small particles, which the creature then digests. The majority of invertebrates are detritivores. The other two types of decomposers are scavengers and saprophytes.




